As uses of artificial intelligence in healthcare keep evolving, robotics and AI-powered robots are gaining momentum due to their capacity to perform accurately and effectively in some of the most important fields of medicine.
From conducting surgeries to streamlining supply delivery, from carrying out genetic testing to collecting data to improve diagnostics, AI robots leveraged for healthcare purposes are helping ease a lot of the burden off the shoulders of professionals while giving them more time to focus and patient care.
Today -and increasingly in the upcoming years-, the impact of AI and robotics will transform almost every aspect of the healthcare industry, contributing to promoting long-term well-being to an overstressed workforce and an aging population of patients.
How are Robots and AI used in Healthcare?
Currently, robots that are being used in the healthcare sector can be reduced to three basic types: Surgical-Assistant Robots, Exoskeletons (or Modular Robots), and Autonomous Mobile Robots. Each of these types is aimed at tackling a different set of issues and challenges in healthcare. Below, we will see a brief definition of them and explore in detail how they are being leveraged for different medical purposes.
3 Examples of AI and robotics in healthcare
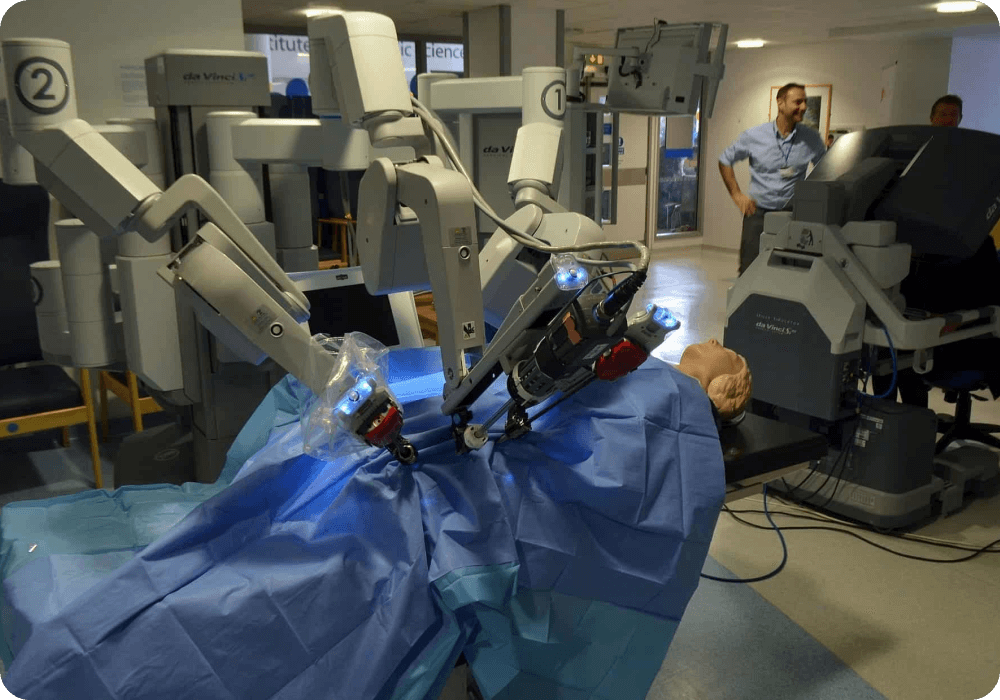
1. Surgical-Assistant Robots
Beginning with robots assisting surgeons in the 1980s, the use of these types of medical robots is growing steadily, and seeing them in operating rooms is becoming increasingly common. The market leader in surgical robots is the North American company Intuitive Surgical, which was founded in 1995 and has an annual revenue that approaches 6 billion dollars.
Though initial prototypes of surgical-assistance robots have existed for more than three decades, the recent advance in motion control technologies has allowed them to gain the outstanding levels of precision they are showing today. With their AI capacity and enhanced-vision technologies, these robots are helping surgeons achieve greater levels of speed and accuracy.
Surgeries performed with the assistance of robots are generally minimally invasive, involving the torso, and mainly focused on soft tissues. Assistant-surgeon robots can lock themselves into the internal place of intervention. From there, surgeries are performed via remote control. This type of robot-assisted surgery has proved successful at reducing infections.
On the other side, there are preprogrammed robotic devices that perform regular orthopedic surgeries. Most of these robots have been trained through AI modeling, which enables them to ensure more predictable results and gradually gain expertise on how to perform specific orthopedic surgeries.
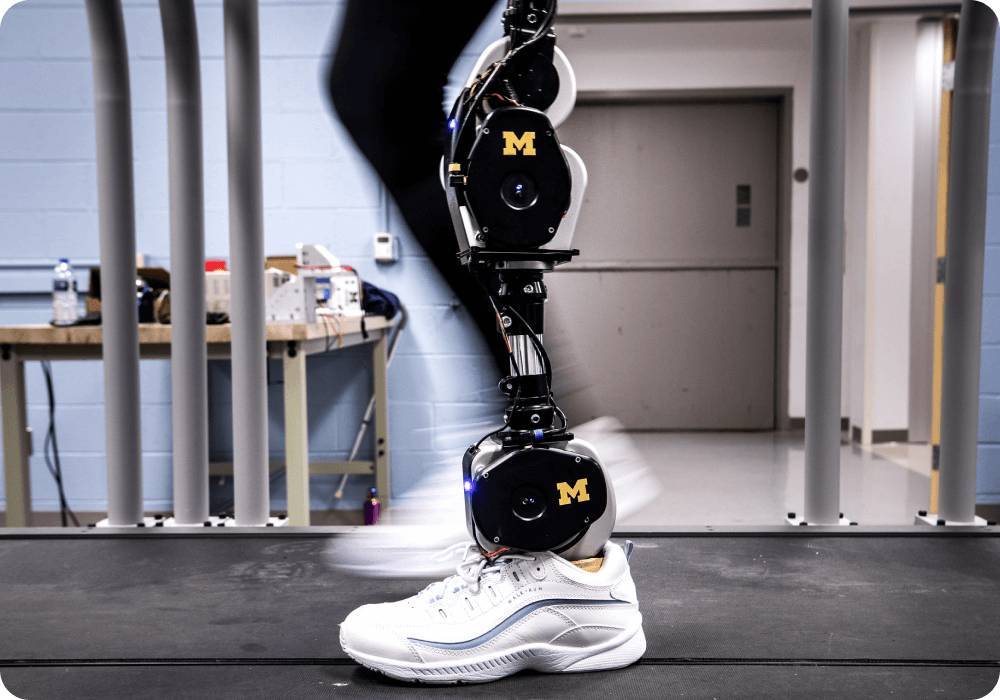
2. Modular Robots (Exoskeletons and Prosthetics)
Modular Robots are mostly designed to aid recovery and help during the rehabilitation process of patients that have suffered strokes, traumatic brain injuries, paralysis, or are struggling against impairments caused by multiple sclerosis. They can, for example, use sensors placed on the skin to detect tiny electric signals in a patient’s body, that are then “translated” into movements at the joints.
Powered by artificial intelligence and equipped with depth cameras, exoskeletons can bring enhanced monitoring as patients go through the different stages of recovery. They can follow up on markers as patients engage in prescribed exercises, accurately measuring motion, and tracking overall progress with an accuracy that is simply impossible to achieve for human beings. These capacities can be used to provide coaching and guidance.
Today, exoskeletons are on the rise, and they are likely to play a prominent role in the upcoming years as brain-machine connectivity keeps evolving. Among the leading companies in this field, one of the most well-known is the Japanese Cyberdyne, which fabricates HAL (Hybrid Assistive Limb). These devices are used by patients who suffer from
spinal cord injuries, cerebrovascular diseases, traumatic brain injuries, and other neuromuscular diseases, and can help these patients move a leg by merely thinking of moving their leg.
Not long ago, this would have sounded like a science fiction device (yes, Robocop), but this technology is already a fast-evolving reality.

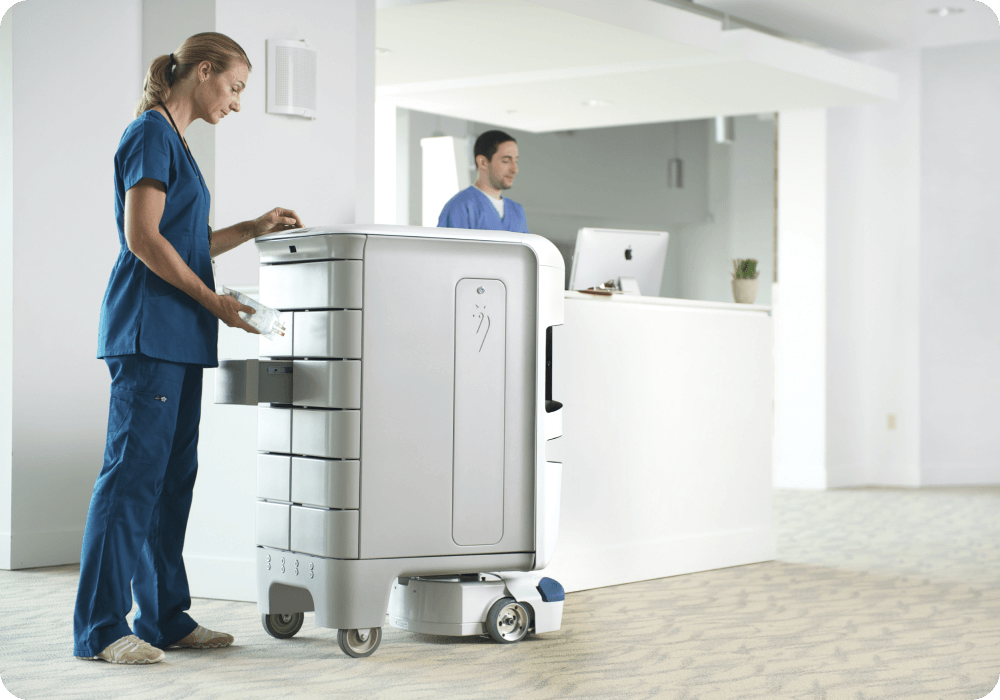
3. Autonomous Mobile Robots
It is no secret for anyone in the healthcare industry that professionals are suffering from high amounts of stress, especially since the pandemic. So the main goal of Autonomous Mobile Robots today is to ease some of the burdens on healthcare workers.
Provided with sensors and cameras that allow them to “perceive” their surroundings, AMRs make real-time decisions as they move through hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities. Aside from built-in maps and onboard sensors, they communicate with elevators, automatic doors, or alarms by using Wi-Fi.
These robots are tackling tasks such as restocking, taking the trash out, or disinfecting surfaces (such as the already widely used UV Light Disinfection Robot). Other robots reduce physical strain by helping with heavy lifting tasks such as moving beds or even patients.
One of their most important benefits is that they can make the workspace safer for professionals, by taking on risky tasks such as transporting supplies and linens that could have been exposed to pathogens and delivering medications, laboratory specimens, or other sensitive materials.

The Future of Healthcare: Humans, Robots, and AI Collaborating Together
Though we have listed those we consider the most important examples of AI and robotics being used in healthcare today, the cases above are far from exhausting the spectrum of what these technologies combined can offer the healthcare industry.
Some other cases of the expanding uses of AI and robotics in healthcare:
- Leveraging their ability to process enormous amounts of data to deliver a more accurate diagnosis.
- Providing care and support to elderly patients (helping them remember when to take medication or offering emotional support).
- Lend a hand to nurses so that they can gain focus on the more emotional, human aspects of patient care by assisting them with simple yet vital tasks such as taking blood and recording temperature.
- Allowing for remote treatment.
Of course, and specialists tend to agree on this, none of this means that we should expect a future dominated by robot doctors. As the examples we have explored above show, the role of AI robots in healthcare is to assist human doctors rather than replace them. Humans, artificial intelligence, and robots working together can create a better future for healthcare.
Contact us for Artificial Intelligence Development Services and other Software Development Services.